Benzodiazepines – Pharmaceutical-Grade Central Nervous System Depressants
Benzodiazepines are a category of psychoactive drugs that directly affect the central nervous system. These compounds enhance the effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which results in a calming effect on the brain and body. Due to their rapid onset and effectiveness, benzodiazepines are widely prescribed in modern medicine. Some of the most common examples include Alprazolam, Diazepam, Lorazepam, and Clonazepam.
These medications play a crucial role in managing a variety of mental and neurological disorders.

Primary Uses of Benzodiazepines
Doctors prescribe benzodiazepines for multiple therapeutic purposes. These include the treatment of anxiety disorders, where the drug acts swiftly to calm excessive neural activity. Patients suffering from insomnia also benefit from benzodiazepines as they improve both sleep onset and duration. For individuals dealing with seizure disorders, these drugs act as effective anticonvulsants. In cases of alcohol withdrawal, benzodiazepines reduce symptoms such as agitation and tremors. Furthermore, they are often used to treat muscle spasms caused by neurological conditions.
Because of their versatility, benzodiazepines remain a staple in short-term pharmacological interventions.
Side Effects and Risks
Despite their benefits, benzodiazepines come with several risks. Common side effects include drowsiness, fatigue, dizziness, and impaired coordination. Long-term use increases the risk of dependence, tolerance, and withdrawal symptoms. Cognitive decline and memory issues may also occur. In elderly patients, the risk of falls and confusion is higher. The combination of benzodiazepine with alcohol or other depressants can lead to dangerous respiratory suppression and should be avoided.
Responsible usage under medical supervision is essential to minimize these risks.
Safe Use and Best Practices
To use benzo safely, follow the prescribed dosage exactly as directed by a healthcare provider. These medications should only be used for short durations unless specifically advised otherwise. Alcohol and other sedatives must be avoided during treatment. Patients should monitor their response to the medication closely and report any unusual side effects to their doctor immediately.
By following proper guidelines, patients can safely benefit from the therapeutic effects of this drug.
Showing all 8 results
-
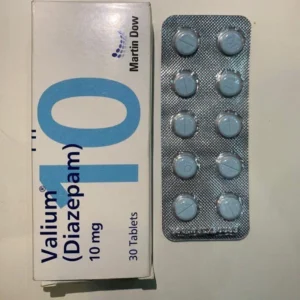
10mg Valium – Diazepam – PHARMA
Price range: $150.00 through $570.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Alprazolam
Price range: $210.00 through $1,000.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

BROMAZOLAM
Price range: $200.00 through $900.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

ETIZOLAM POWDER
Price range: $300.00 through $2,000.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Flualprazolam
Price range: $170.00 through $800.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Flubromazolam
Price range: $350.00 through $1,200.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Methylmethaqualone
Price range: $150.00 through $1,300.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Nitrazolam
Price range: $140.00 through $1,100.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
